


Manage and monitor processes, programs, files, directories and file systems, log changes in files size, directories content, and checksums.
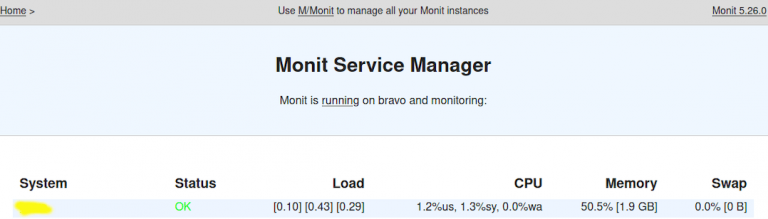
Monit is an open source monitoring tool for Linux operating systems. This is how looks monit after adding all process for monitoring.Using Monit process monitoring on Ubuntu/Debian info : 'nginx' start: /etc/init.d/nginx Monit Screenshot # tail -f /var/log/monit $ sudo tail -f /var/log/monit.log Sample Output info : Starting monit HTTP server at You can verify that monit service is started by checking log file. # /etc/init.d/monit restart $ sudo /etc/init.d/monit restart # monit -t $ sudo monit -tĪfter fixing all possible errors, you can type the following command to start the monit service. When you get message like “ Control file syntax OK“, or if you see no errors, you can proceed ahead. If found any errors fix them, it’s not so tough to figure out what’s went wrong.

Once you’ve configured all programs for monitoring, check monit syntax for errors. If 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout If failed host 127.0.0.1 port 22 protocol ssh then restart If 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout SSHD check process sshd with pidfile /var/run/sshd.pid If failed host 127.0.0.1 port 3306 then restart Start program = "/etc/init.d/mysqld start" Stop program = "/etc/init.d/nginx stop" MySQL check process mysqld with pidfile /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid Start program = "/etc/init.d/nginx start" Stop program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 stop" Nginx check process nginx with pidfile /var/run/nginx.pid Start program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 start" with timeout 60 seconds If 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout Apache2 check process apache with pidfile /run/apache2.pid Start program = "/etc/init.d/httpd start" Apache check process httpd with pidfile /var/run/httpd.pid
#Monit web port how to
Once monit web interface correctly setup, start adding the programs that you want to monitor into the /etc/nf under ( RedHat/CentOS/Fedora) and /etc/monit/monitrc file for ( Ubuntu/Debian/Linux Mint) at the bottom.įollowing are some useful configuration examples for monit, that can be very helpful to see how a service is running, where it keeps its pidfile and how to start and stop a service etc.
#Monit web port password
Then enter user name as “ admin” and password as “ monit“. Now, you will able to access the monit web interface by navigating to the “ or “ “. # /etc/init.d/monit start $ sudo /etc/init.d/monit start Once you’ve configured it, you need to start the monit service to reload the new configuration settings. Use address localhost # only accept connection from localhostĪllow localhost # allow localhost to connect to the server andĪllow admin:monit # require user 'admin' with password 'monit'Īllow # allow users of group 'monit' to connect (rw)Īllow readonly # allow users of group 'users' to connect readonly Next, uncomment the following section and add the IP address or domain name of your server, allow anyone to connect and change monit user and password or you can use default ones. # vi /etc/nf $ sudo vi /etc/monit/monitrc Open this file using your choice of editor. The main configuration file of monit located at /etc/nf under ( RedHat/CentOS/Fedora) and /etc/monit/monitrc file for ( Ubuntu/Debian/Linux Mint). To enable web interface you need to make changes in monit configuration file. Monit has it’s web interface that runs on port 2812 using web server. It is designed to monitor the running services in every 2 minutes and keeps the logs in “ /var/log/monit“. Monit is very easy to configure, in fact the configuration files are created to be very easily readable and making them easier for users to understand.
#Monit web port install
On RedHat/CentOS/Fedora/ # yum install monit On Ubuntu/Debian/Linux Mint $ sudo apt-get install monit Step 2: Configuring Monit For Ubuntu/Debian/Linux Mint user’s can easily install using apt-get command as shown. Once you’ve added epel repository, install package by running the following yum command. By default, Monit tool is not available from the system base repositories, you need to add and enable third partyepel repository to install monit package under your RHEL/CentOS systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
